Defamation can take the form of libel or slander. Slanderous statements are verbal, while libelous comments are written. Unlike slander, libel can be spread through any medium (blog comment, speech, or television broadcast).
Are you familiar with the term seditious libel? In 1798, the Sedition Act made printing lies about the government, the president, or Congress illegal. In a later decision, the Supreme Court modified this rule to hold that a statement against a public figure is only libelous if it is deliberately false or made with a reckless disregard for the truth.
!
The term defamation refers to the dissemination of false statements as facts that cause damage to individuals and businesses. It is possible to sue for defamation if the act damages someone's reputation or economic opportunities.
Examples of Libel
Social media has multiplied the chances of libel. But in the United States, the media is one of the most significant sources of libel. You'll find many libel claims filed against professional publications if you Google active libel cases.
Libel cases must contain both false and untrue information for them to succeed. Libel cases can be per se or per quod. Libel, per se, refers to content that defames someone's character outright.
Per quod means "undercover" in Latin, and libel per quod refers to situations in which the contents are unclear but serve to defame an individual. It is much easier to prove and prosecute libel per se cases.
Public figures and celebrities are often targets of libel. They are less likely to win libel suits than ordinary people because the courts find public figures less deserving of reputation protection.
!
The rationale is that public figures seek public attention and accept a measure of risk for negative attention. Public figures can refute libelous claims, unlike the public.
Here are a few famous libel cases:
J.K. Rowling vs. The Daily Mail: According to the bestselling author, the Daily Mail falsely accused her of lying in a charity article she wrote.
Russell Brand vs. The Sun: An article in the publication stated that the actor had cheated on his then-girlfriend, Jemima Khan, in November 2013.
Kate Winslet vs. The Daily Mail: The Daily Mail falsely claimed that Winslet lied about her workout routine, which she accused them of falsifying. According to reports, £25,000 was paid out.
Rebel Wilson vs. Bauer Media: As a result of her lawsuit against Bauer Media, Rebel Wilson was awarded an amount of AUD 4.7 million in September 2017.
Examples of Slander
The act of oral defamation involves making untrue statements about another person that causes quantifiable damage. Slander is most common at work because false statements can hurt someone's career. Examples include:
- Business owners could be defamed if they did not participate in unethical and illegal activities
- Accusing a colleague of tax defaults
- Accusing someone of incompetence could cost them their job or lead to ridicule or contempt
- Falsely accuse a coworker of sexual harassment
Defense for Defamation
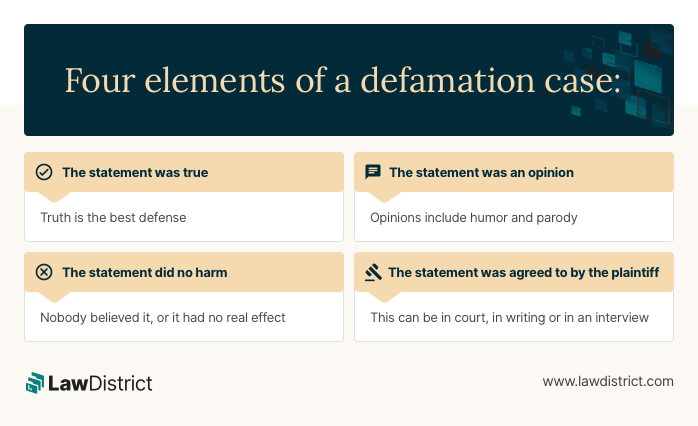
Some victims may send a cease-and-desist letter as a scare tactic. But if you sue for defamation, you need to prove four elements. Each of the four elements must be challenged to establish a defamation defense:
- The statement was true: Truth is the best defense for defamation lawsuits. In an absolute defense, the court will rule in favor of the defendant if the statement is true.
- The statement was an opinion: It will not be considered defamatory if it is shown as an opinion piece (e.g., humor, parody, cartoon, caricature).
- The statement did no harm: The statements may have been malicious and false, but if no one believed them, there was no harm to you.
- The statement was agreed to by the plaintiff: It would also be a defense if the plaintiff agreed at some point with the statement. An interview or perhaps a written piece could be used for this.
Read More: Famous Cease and Desist Letters
Get a Cease and Desist Letter Here
Criminal Defamation Laws by states
Some states have different rules regarding how they treat defamation, make sure you check your state’s laws in the table below.
| State
|
Defamation Law
|
| Alabama
|
Ala. Code § 13a-11-160, 163
|
| Arkansas
|
§ 16-63-207 - Libel and Slander
|
| Arizona
|
23-1325 Defamation; Damages
|
| Arkansas
|
§ 16-63-207 - Libel and Slander
|
| California
|
CACI No. 1704. Defamation Per Se
|
| Colorado
|
13-25-125.5. Libel and Slander
|
| Connecticut
|
Sec. 52-237. Damages in Actions for Libel
|
| Delaware
|
2014 Delaware Code Title 10
|
| Florida
|
Fl St § 836.01-.06, 836.09-.12
|
| Georgia
|
Georgia Code § 51-5-1 (2021)
|
| Hawaii
|
Hawaii Revised Statutes § 657-4 (2021)
|
| Idaho
|
Id St §18-4802, 4809
|
| Illinois
|
Il St Ch 720 § 300/1
|
| Indiana
|
2021 Indiana Code Title 34
|
| Iowa
|
Chapter 659 Libel and Slander
|
| Kansas
|
Kan. Stat. § 21-6103
|
| Kentucky
|
Ky St § 432.280
|
| Louisiana
|
La R.S. 14:47
|
| Maine
|
Title 24-A, §2157: Defamation
|
| Maryland
|
Subtitle 5 - Defamation
|
| Massachusetts
|
MGL C.218, § 21, MGL C.231, §§ 91-94 , MGL C.258, § 10(C), MGL C.260, § 4
|
| Michigan
|
Mi St 750.370, 371
|
| Minnesota
|
609.765 Criminal Defamation
|
| Mississippi
|
97-3-55 - Libel; Penalty: 2013 Mississippi Code
|
| Missouri
|
RSMO Section 516.140
|
| Montana
|
Part 8. Libel and Slander
|
| Nebraska
|
2021 20-209 - Libel, Slander, Or Invasion of Privacy; One Cause of Action
|
| Nevada
|
NRS 200.510 Definition; Penalties; Truth
|
| New Hampshire
|
2017 New Hampshire Revised Statutes Section 644:11 - Criminal Defamation
|
| New Jersey
|
2013 New Jersey Revised Statutes Section 2a:14-3 - 1 Year; Libel or Slander
|
| New Mexico
|
2021 New Mexico Statutes Article 7 - Libel and Slander
|
| New York
|
Article 7 Miscellaneous Rights and Immunities Civil Rights (CVR) Chapter 6
|
| North Carolina
|
Chapter 99 - Libel and Slander
|
| North Dakota
|
N.D. Cent. Code § 14-02-03
|
| Ohio
|
Section 2739.01 - Ohio Revised Code
|
| Oklahoma
|
§21-781. False Rumors - Slander - Penalty
|
| Oregon
|
Oregon Revised Statutes § 135.733 (2021) - Defamation
|
| Pennsylvania
|
Defamation - Title 42 - Pa General Assembly
|
| Rhode Island
|
Chapter 9-6-9 - Truth as Defense to Libel Or Slander
|
| South Carolina
|
2012 South Carolina Code of Laws Section 16-7-150 - Slander and Libel.
|
| South Dakota
|
2013 South Dakota Codified Laws Chapter § 20-11-3 libel Defined. § 20-11-4 slander Defined.
|
| Tennessee
|
2014 Tennessee Code Chapter 24 - Libel and Slander
|
| Texas
|
Title 4. Liability In Tort Chapter 73. Libel
|
| Utah
|
2021 Utah Code Section 2 - Libel and Slander Defined.
|
| Vermont
|
Title 12: Court Procedure Chapter 199: Defamation
|
| Virginia
|
Code Of Virginia Code - Article 4. Defamation
|
| Washington Dc
|
§ 31–2231.05. Defamation
|
| Washington State
|
2005 Revised Code of Washington - Chapter 9.58 RCW: Libel and Slander
|
| Wisconsin
|
939.22. 942.01 Defamation
|
| Wyoming
|
Chapter 29 - Libel and Slander
|
Sources:
The Sedition Act of 1798 | US House of Representatives
JK Rowling sues Daily Mail for libel over 'single mother' article | The Guardian
Russell Brand wins libel damages from 'Sun' newspaper | EW



